Verify Sender Domains
Before you can use SmartLink to send marketing emails, your sender domain (the portion after the "@" in an email address, such as "example.com") has to be verified. Domain authentication can ensure the authenticity and legitimacy of emails, reduce the probability of emails being blocked or marked as spam, thereby improving email deliverability. In addition, domain names that include organization or product information are more likely to be trusted, lowering the unsubscription rate caused by a lack of trust.
For sender domains, SmartLink requires DKIM authentication and SPF authentication is recommended.
Before verifying a domain, make sure that the domain has been registered and that you have administrative privileges for the domain.
DKIM authentication
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is an email security standard designed to ensure that emails claiming to come from a specific domain are indeed authorized by the owner of that domain. DKIM uses public-key cryptography to sign an email with a private key. Recipient servers can then use a public key published to the domain's DNS to verify that all parts of the email have not been modified in transit.
SPF authentication
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an email authentication standard designed to prevent email spoofing by checking if the sender's IP address matches the sender's domain. To set-up SPF, you need to publish a DNS TXT record to your domain configuration. This record contains a list of servers that are authorized to send emails from your domain. When email service providers receive an email through SMTP from your domain, the source IP address of the email will be compared with the IP addresses in the DNS record of your domain to ensure that the email is sent from an authorized server.
DMARC authentication
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) is an email identity authentication standard designed to improve email security. DMARC records are set by the domain owner to tell receiving servers how to handle outgoing messages from your organization that did not pass SPF or DKIM authentication. DMARC provides the domain owner with information about email authentication failures related to their domain by including a special DMARC reporting address in the email header. This helps the domain owner better understand the email traffic of their domain, and take the appropriate steps to reduce fraudulent emails and phishing attacks.
For more information, see Define your DMARC record.
If DMARC has already been configured, modify the configuration to use the TXT record on SmartLink, otherwise add a new TXT record.
Gmail Domain Monitoring Configuration
Google Postmaster Tools is a free service provided by Google that helps domain owners monitor the performance of emails delivered to Gmail.
Via Postmaster Tools, we can track the following key metrics:
- Email delivery success rate and spam rate
- Domain and IP reputation
- User feedback and complaint rates
- Authentication (DKIM, SPF, DMARC) status
- Gmail filtering trends
This data helps us understand whether emails are being successfully delivered to recipients' inboxes and allows us to promptly identify potential delivery issues.
Verify domain name
At the top of the SmartLink sidebar, click your account name, then select Project settings.
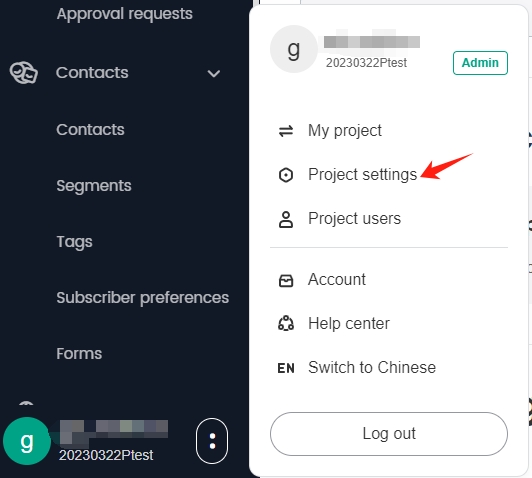
In the Project settings page, select Settings under Email domains.
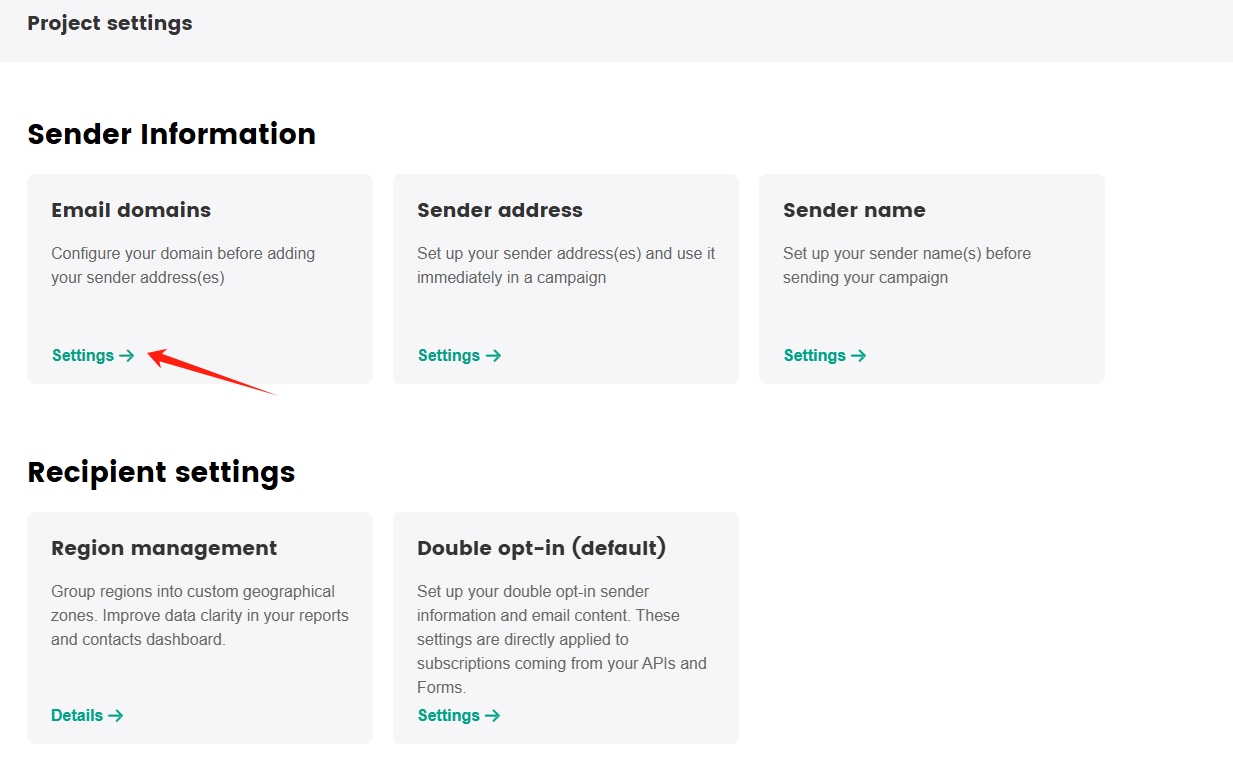
In the Email domains page, click Add Domain to add the domain that you want to verify.
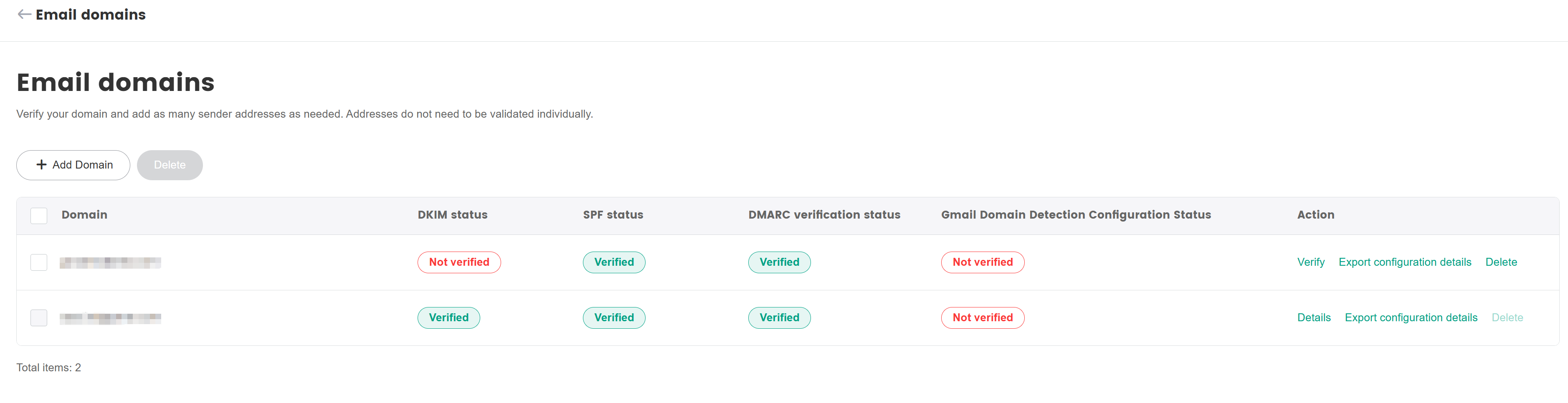

The domain administrator is required to log in to the domain name registrar's console and add the record value obtained from SmartLink to the DNS configuration of the domain.
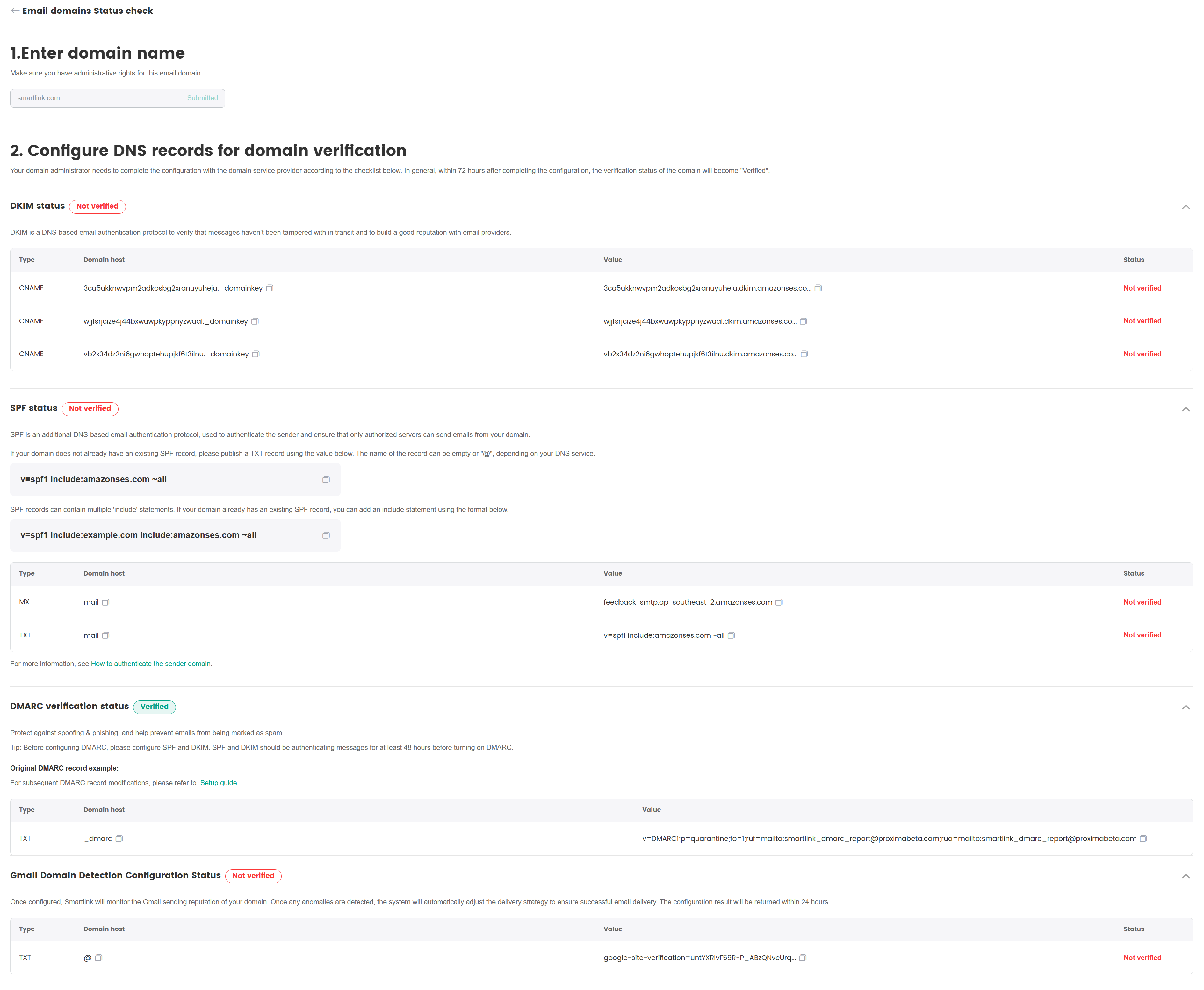
After completing the configuration, SmartLink will automatically update the verification status. After all records are verified, a daily sending limit will be allocated automatically.
By default, the number of emails sent from each domain cannot exceed 3 million in 24 hours. You can contact SmartLink_service@proximabeta.com to adjust the quota.